Dataset Service
Before you begin
In order to use the features in this section you need to have an active Spojit account with a Business plan. If you don't have an account you can checkout out the pricing and register here. If you already have an account you can login here.
The Dataset service allows you to read, write and delete columns/rows to a collection of data (database table).
The following example configuration shows you how to add a dataset and how to configure the Dataset service to insert, update, delete and find data within the dataset.
Creating a dataset¶
Before starting to use the dataset service a dataset needs to be created in the Spojit platform. Select "Datasets" on the left side bar and click "+ Dataset" to add a new dataset. Add a name for the dataset and define the columns:
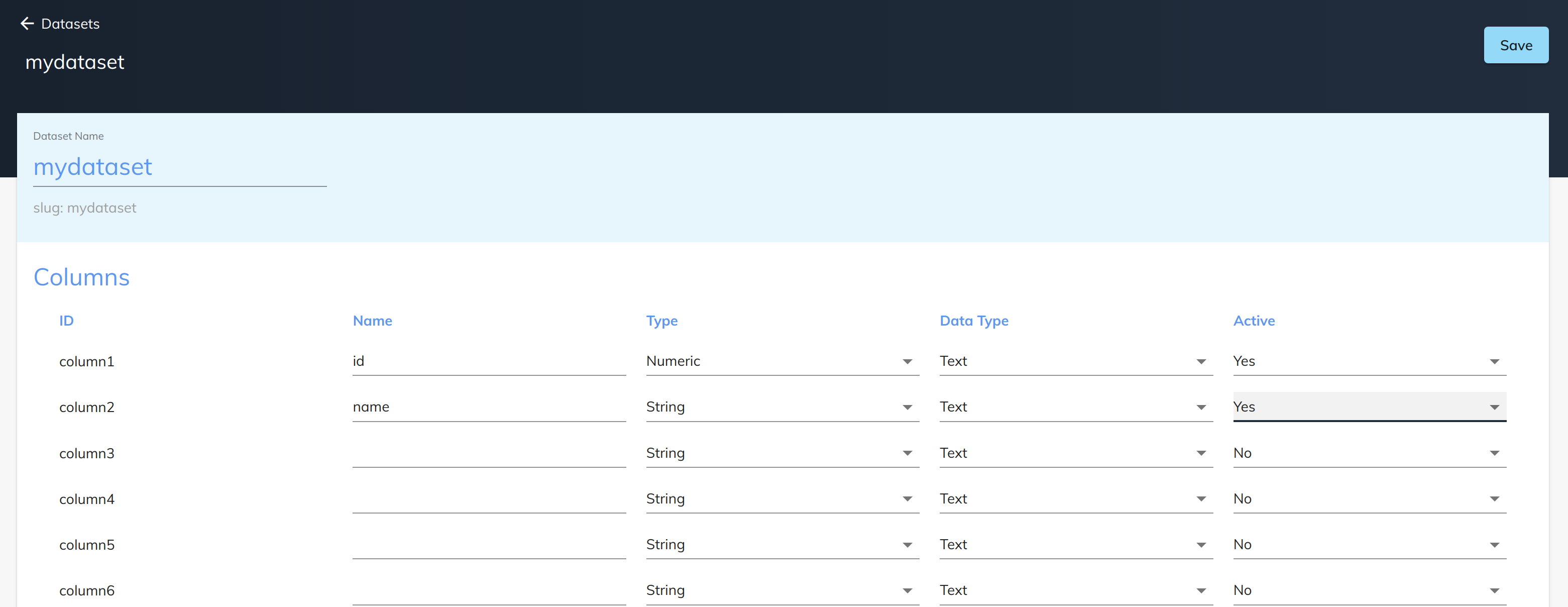
Column Type¶
The column type is the type of data that is stored in the column.
| Option | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| STRING | A text value | "car" |
| NUMERIC | A numerical value | 123456 |
| BOOL | A boolean value | TRUE or FALSE |
| ARRAY | A list of values or objects | ["bike", "boat", "car"] |
Data Type¶
The data type is the type of data used for statistical and training purposes.
| Option | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| TEXT | Free forms words or sentences. | "The sun is hot in the summer!" |
Important
Inactive columns will be cleaned a regular intervals.
Once the columns are defined make sure that they are active in order to be used. After a dataset is saved you will be able to use it in any workflow.
Dataset Row Object¶
When dealing with a row in the dataset an object with be used with the fields matching the columns specified in the dataset configuration.
Reserved columns (fields)¶
The following reserved names can not be used to name a column or be a field in the dataset row object as they are automatically generated for an object:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| _id | Internal ID generated for this row. |
| _createdAt | The interal creation datetime for this row (UTC). |
| _updatedAt | The interal updated datetime for this row (UTC). |
Info
Although you can not create/update or delete any reserved fields they can be used for querying the dataset.
Example dataset row object¶
If you have the columns id and name from the creating a dataset example above the object would consist of the following (with the reserved fields added):
{
"id": 1,
"name": "delectus aut autem",
"_id": "60792518693cf2625e7530b2",
"_createdAt": "2021-04-16T05:48:08+00:00",
"_updatedAt": "2021-04-16T05:48:08+00:00"
}
Dataset Querying Criteria¶
You can query a dataset with critier to find a record to update or to search for records within the dataset.
The following operators can be used:
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
| eq | Equal to |
| neq | Not equal to |
| lt | Less than |
| lte | Less than equal to |
| gt | Greater than |
| gte | Greater than equal to |
These operators can be chained to produce more specific results.
Primary Keys¶
The internal primary key (id) will always be generated automatically but if you want to pair it with an external primary key (or other unique identifier) the "Upsert" method can be used with criteria to identify it.
For example if the "Upsert" method is setup in the following way:

The record will be created if the value for external_id doesn't exist in the id column or updated if it does. Two or more columns can also be used to have a composite primary key.
Service Methods¶
The dataset service has various methods add to and perform actions on data in a dataset.
Insert a row¶
Inserting a row will add a new record into the dataset.
| Option | Description | Default | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| Method | Select "insert" to insert a row into the dataset. | - | TRUE |
| Dataset | Select the name of the dataset you wish to use. | - | TRUE |
Example configuration and mapping
The following example shows you how to configure the Dataset Service to insert a record.

The schema can be whatever you wish to insert into the dataset with the fields matching the columns specified in the Dataset Configuration. For this example we are going to create an OBJECT schema with the specified fields:
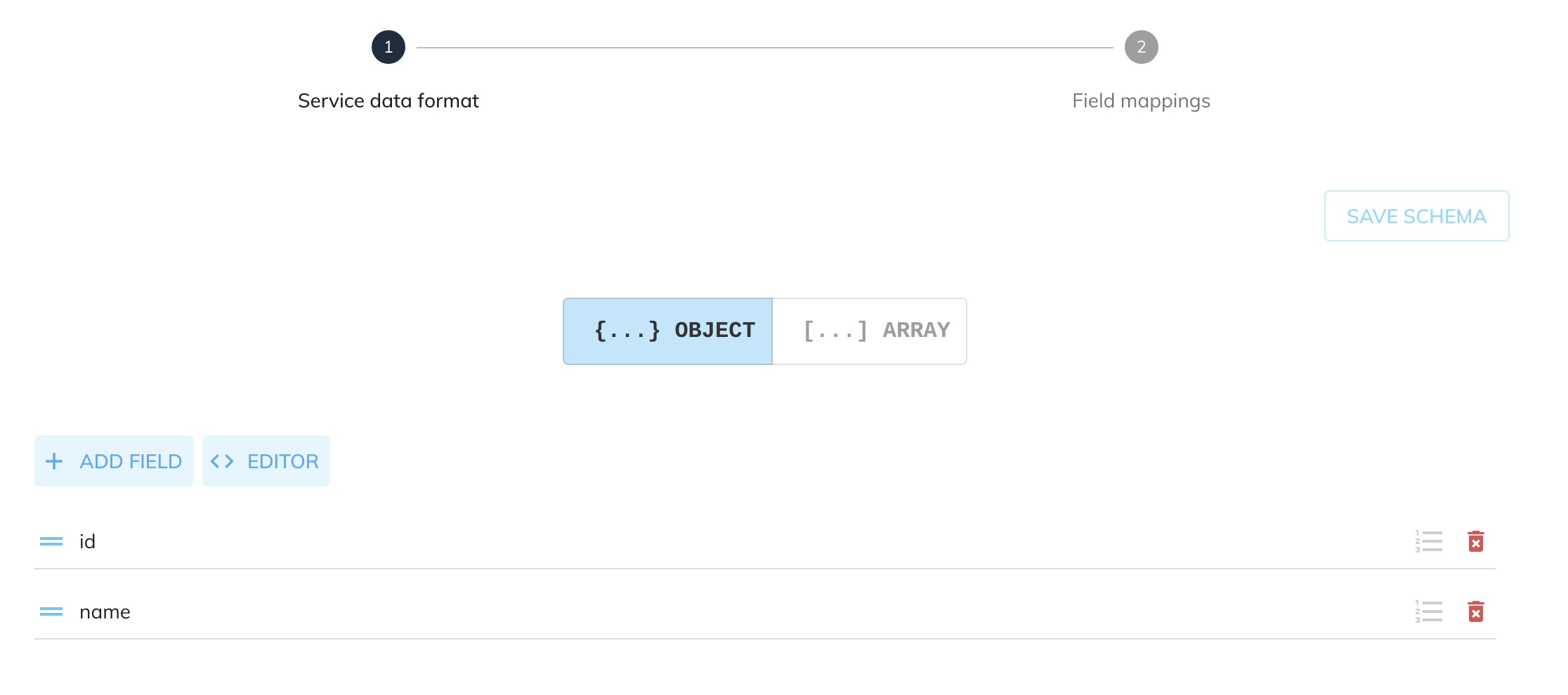
Given the following source data from another service:
We can map the applicable fields with the schema object:

Update a row¶
Updating a row will update a record in the dataset.
| Option | Description | Default | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| Method | Select "update" to update a row in the dataset. | - | TRUE |
| Dataset | Select the name of the dataset you wish to use. | - | TRUE |
| Criteria | Criteria used to find existing records to update. | - | FALSE |
Example configuration and mapping
The following example shows you how to configure the Dataset Service to update a record given an id of 1.

The schema can be whatever you wish to update into the dataset with the fields matching the columns specified in the Dataset Configuration. For this example we are going to create an OBJECT schema with the specified fields:
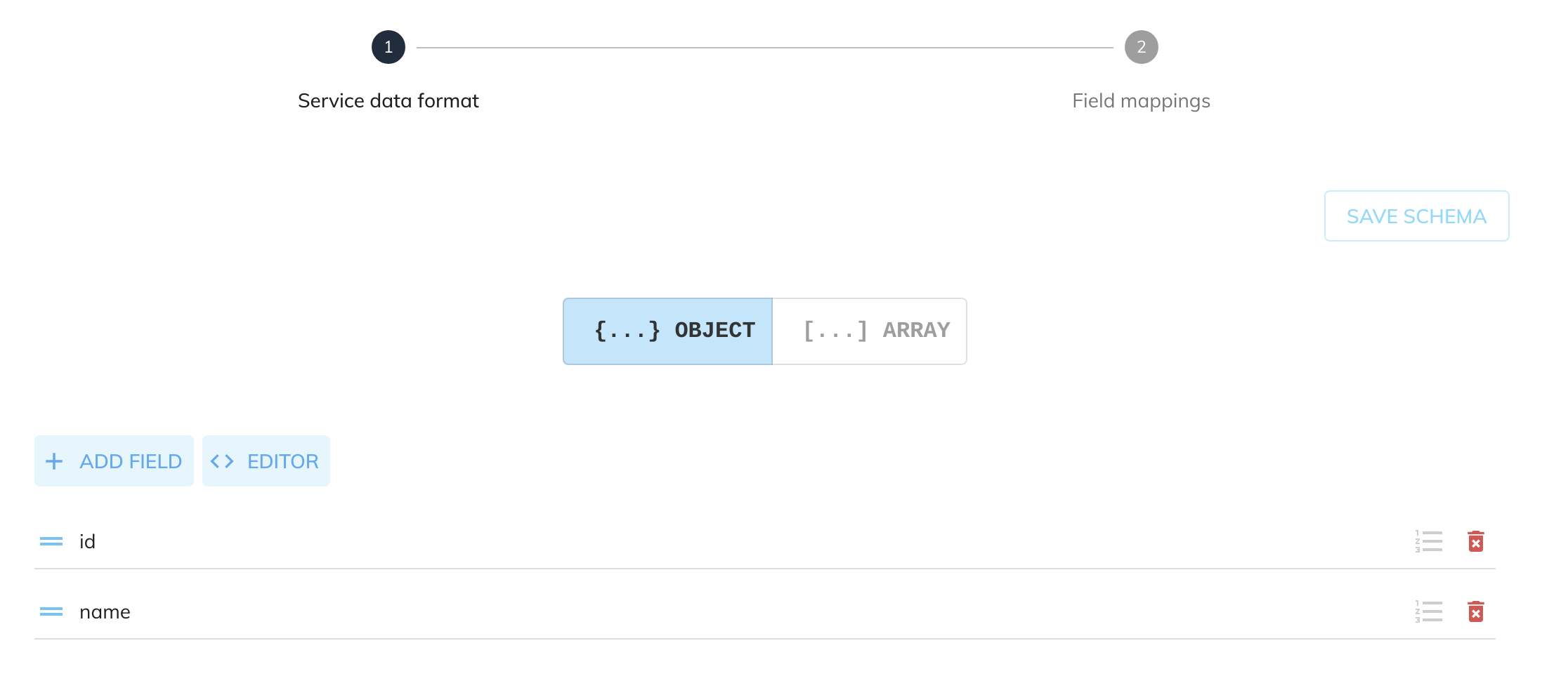
Given the following source data from another service:
We can map the applicable fields with the schema object:

Upsert a row¶
Upserting a row will either create a record in the dataset if it doesn't exist or update a record if it already exists.
| Option | Description | Default | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| Method | Select "upsert" to upsert a row in the dataset. | - | TRUE |
| Dataset | Select the name of the dataset you wish to use. | - | TRUE |
| Criteria | Criteria used to find existing records to update. | - | FALSE |
Example configuration and mapping
The following example shows you how to configure the Dataset Service to upsert a record given an id from an external entity (see above about primary keys).

The schema can be whatever you wish to upsert into the dataset with the fields matching the columns specified in the Dataset Configuration. For this example we are going to create an OBJECT schema with the specified fields:
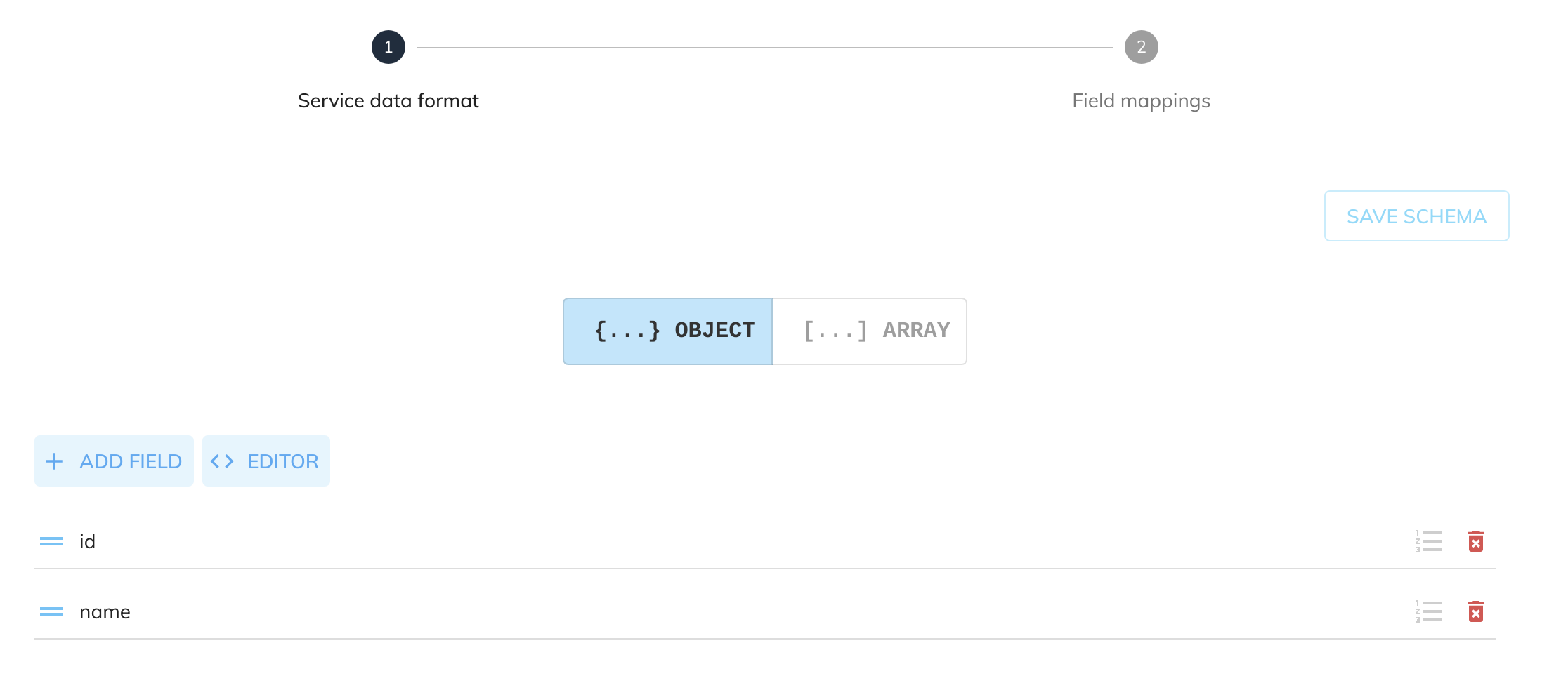
Given the following source data from another service:
We can map the applicable fields with the schema object:

Delete a row¶
Deleting a row will remove a record from the dataset if it exists.
| Option | Description | Default | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| Method | Select "delete" to delete a row in the dataset. | - | TRUE |
| Dataset | Select the name of the dataset you wish to use. | - | TRUE |
| Criteria | Criteria used to find existing records to delete. | - | FALSE |
Example configuration and mapping
The following example shows you how to configure the Dataset Service to update a record given an id of 1.
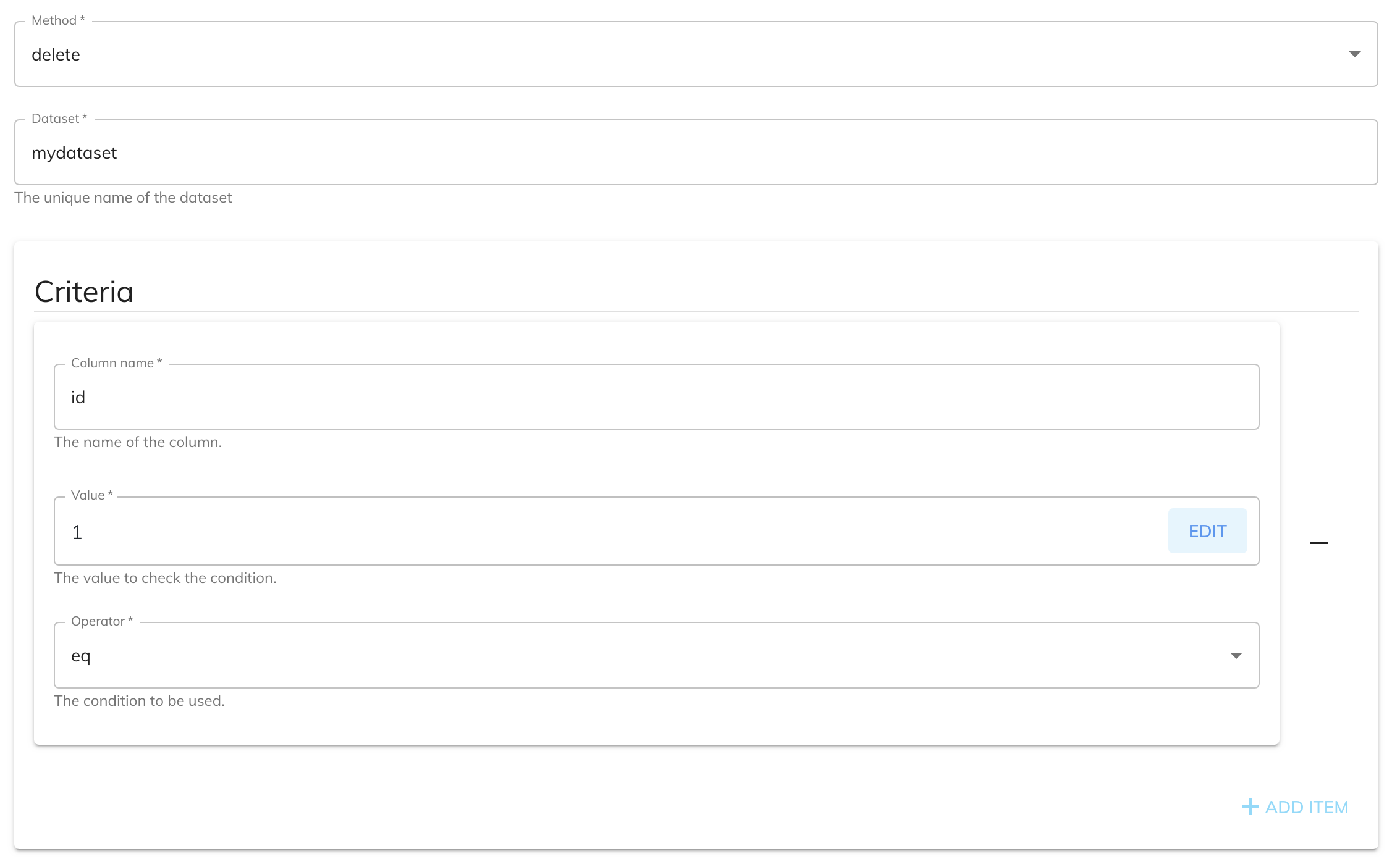
The DELETE method doesn't require any service data setup.
There will be no output data generated by the DELETE method. An error will be thrown if it can't be deleted.
Find one row¶
Find one row will search for and find one record from the dataset if it exists. It will find and return the first matching record. If there are multiple matching rows then "find" should be used.
| Option | Description | Default | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| Method | Select "findOne" to find a row in the dataset. | - | TRUE |
| Dataset | Select the name of the dataset you wish to use. | - | TRUE |
| Criteria | Criteria used to find existing records. | - | FALSE |
Example configuration and mapping
The following example shows you how to configure the Dataset Service to find a record given an id of 1.

The FINDONE method doesn't require any service data setup.
Find rows¶
Find rows will search for and find records from the dataset if they exists. It will find and return all matching records in an array. If you only want one result "findOne" should be used.
| Option | Description | Default | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| Method | Select "find" to find rows the dataset. | - | TRUE |
| Dataset | Select the name of the dataset you wish to use. | - | TRUE |
| Criteria | Criteria used to find existing records. | - | FALSE |
Example configuration and mapping
The following example shows you how to configure the Dataset Service to find records given an colour of "blue".
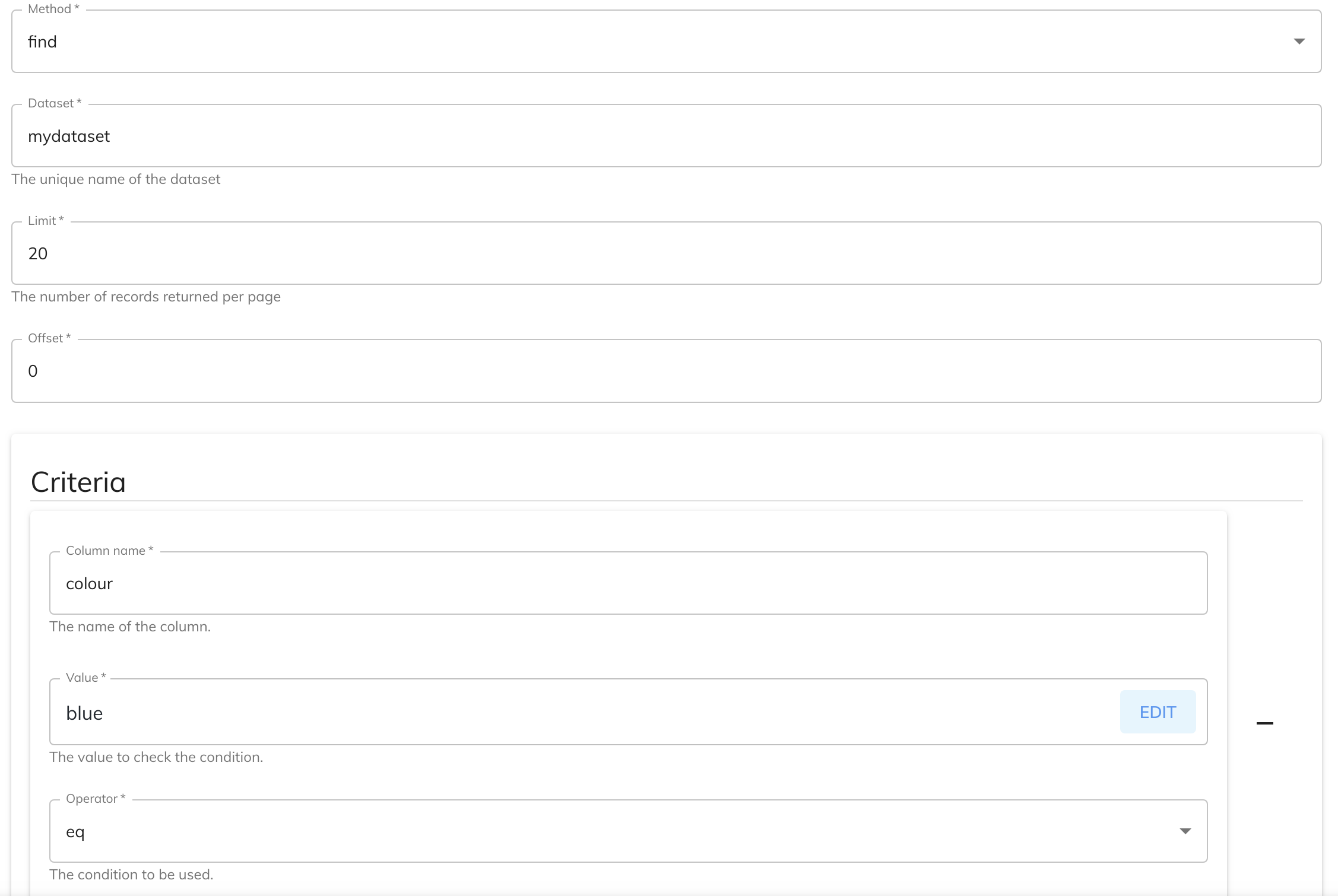
The FIND method doesn't require any service data setup.
In this example the following output will be generated automatically by this service after it is run (note that an array of objects is returned):
{
"data": [
{
"id": 1,
"name": "pants",
"colour": "blue",
"_id": "60792518693cf2625e7530b2",
"_createdAt": "2021-04-16T05: 48: 08+00: 00",
"_updatedAt": "2021-04-16T05: 58: 08+00: 00"
},
{
"id": 2,
"name": "tshirt",
"colour": "blue",
"_id": "60792518693cf2625e7530b2",
"_createdAt": "2021-04-16T05: 48: 08+00: 00",
"_updatedAt": "2021-04-16T05: 58: 08+00: 00"
}
],
"metadata": [
]
}